- 0508 966 622
- help@zoompharmacy.co.nz
- Mon - Fri: 8:30 - 16:00
You are likely familiar with the process of blood clotting and its important part in the bodies healing process. We need our blood to clot when we’ve cut or injured ourselves to stop the bleeding. However sometimes blood clots can form where they shouldn’t – this can lead to serious medical conditions. In this article we will look at what causes blood clots, the types of blood clots and their warning signs.
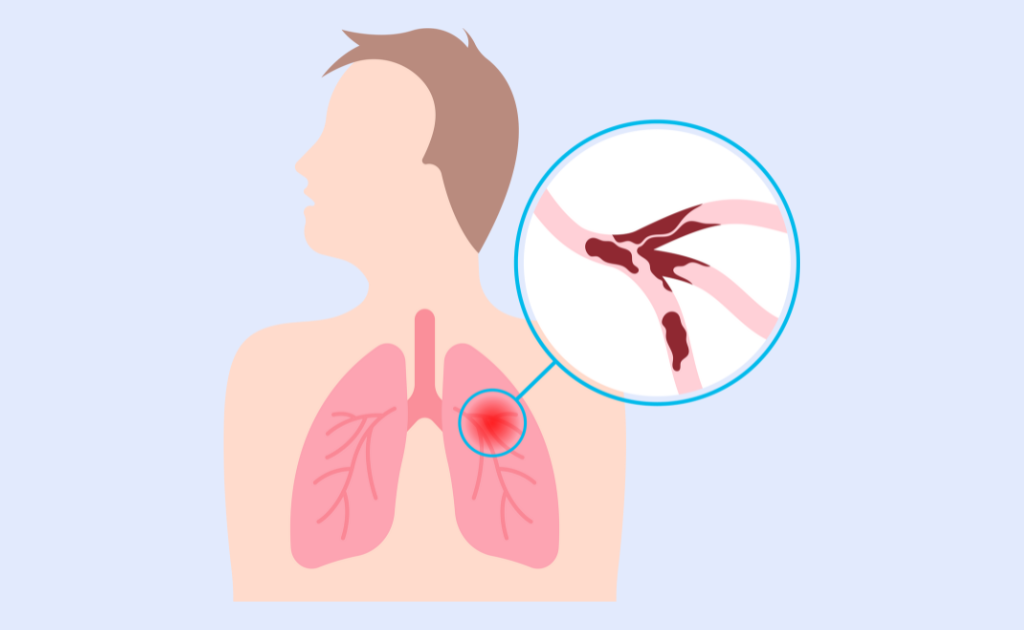
If you are cut or injured your blood will coagulate or thicken, forming a semisolid mass at the site of the bleeding. This is the bodies process to prevent further bleeding from damaged blood vessels and promote healing.
However, blood clots can form inside blood vessels without an injury and may not dissolve. These blood clots can also break off and travel through the circulatory system to your heart, brain, lungs – there is a risk that it may get stuck, preventing blood flow.
Thrombus: stationary blood clots that can block blood flow.
Embolus: blood clots that have broken loose and travelled to another part of the body.
The symptoms of blood clots will vary depending on where in the body the clot is, and in some cases there may be no apparent symptoms. Understanding the most common warning signs of a blood clot will help you know when to see a healthcare professional. Read on to learn the symptoms for different types of blood clots.
A clot can form in the deep veins – blood vessels that carry blood back to your heart. Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) most commonly affects the veins in your lower legs but may occur in the foot, ankle, whole leg, or arm. A blood clot in your leg or arm may have the following symptoms:
If a blood clot in the deep veins breaks loose and travels to your lungs it can result in pulmonary embolism (PE) a serious and potentially fatal condition.
If you have even mild symptoms of DVT you must seek medical attention urgently – this can prevent serious complications such as PE through getting treatment right away.
A blood clot causing a blockage in one of the lungs is known as pulmonary embolism (PE). Typically, this occurs when a blot clot formed in the legs (DVT) comes loose and travels to the lungs. This clot will restrict or block blood flow in the lungs. This condition is very serious and without quick treatment may be fatal. The symptoms of PE may include:
Seek immediate medical attention if you experience any of the symptoms. Call 111 without delay.
If a blood clot occurs in the arteries of the heart, it can block critical blood flow and cause a heart attack. Without oxygen the heart muscles will begin to die, and the longer the blockage remains the greater the damage to the heart. The blockages are usually due to fat, cholesterol and other substances building up in the coronary arteries. These plaques can also rupture, and a blood clot can form on them blocking the artery. The symptoms of a heart attack can vary from mild to severe.
The primary symptom of a heart attack is chest pain or discomfort that continues beyond a few minutes. This pain may come and go initially, be in one or both arms (typically left), and radiate into your neck, back, jaw, stomach, or abdomen.
Additional symptoms to chest pain include:
Women are more likely to experience these additional symptoms than men. They may occur with or without chest pain.
If you are experience some of these symptoms call 111 immediately without delay.
It is possible for blood clots to occur directly in or travel to your brain. If this happens, blood can not bring oxygen to your brain, resulting in hypoxia and causing a stroke. After a few minutes without blood flow your brain will begin to suffer damage. The signs and symptoms of a stroke will usually come on quickly and will depend on what area of the brain is being affected. The acronym BE FAST can be used to help spot the signs of a stroke:
B – Balance loss, or trouble with coordination
E – Eyesight changes, blurred vision, double vision, or loss of vision
F – Face drooping unevenly
A – Arm is weak or numb on one side
S – Speech difficulties, slurred, or unable to speak
T – Time to call 111 immediately
These symptoms are present in 85% of strokes, if you suspect you (or somebody else) might be having a stroke call 111 immediately.
There are risk factors that increase your chances of having a blood clot. These can include:
If you believe you have some form of blood clot seek medical attention and an experts opinion urgently. Diagnosing a blood clot can be difficult and healthcare professionals will be able to examine your symptoms, medical history and run tests to determine the cause. The sooner you get a diagnosis and start treatment the better.
Call 111 Immediately – If you are (or somebody else is) suddenly experiencing the following symptoms call 111 right away:
Resources: